Today’s vast and complex global supply chains connect manufacturers, suppliers, logistics companies, and retailers to meet consumer demand. However, traditional supply chain practices often rely on outdated paper-based systems and siloed data, which can lead to inefficiencies and fragmented information. This lack of traceability and transparency is a major challenge in the industry, potentially leading to delays, errors, and increased costs.
To address these challenges, modern supply chains need a unified view of data that allows them to verify transactions simultaneously and securely, such as updates on production and transportation, while protecting sensitive information. Blockchain technology offers a promising solution to these problems, providing a secure and transparent way to track goods and transactions across the supply chain.
Blockchain 101
Blockchain technology operates as a decentralized and distributed ledger system, which securely registers transactions across numerous computers, guaranteeing data integrity and transparency. The fundamental structure comprises a series of interconnected blocks—each housing a collection of transactions. Once integrated into the chain, a block attains immutability, rendering it impervious to modifications and ensuring robust security. This decentralized architecture of blockchain safeguards data from centralized control, thereby fortifying its resistance to unauthorized tampering and fraudulent activities. Blockchain has inherit transparency and immutability, rendering it a dependable and trustworthy option for registering and authenticating transactions in supply chain management.
Three key blockchain concepts:
- Shared ledger: Constitutes a permanent and scattered record-keeping system accessible across a network. In a shared ledger, transactions are captured only once, thereby eliminating redundancies commonly associated with traditional corporate networks.
- Permission: Serves as a vital mechanism to ensure the security, authentication, and verifiability of transactions. By possessing the capability to control network participation, organizations can more effectively adhere to data protection regulations, such as those outlined in the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) and the European Union General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
- Smart Contracts: These are contractual agreements or predefined rules governing business transactions. These contracts are securely stored on the blockchain and automatically executed as an integral part of a transaction.
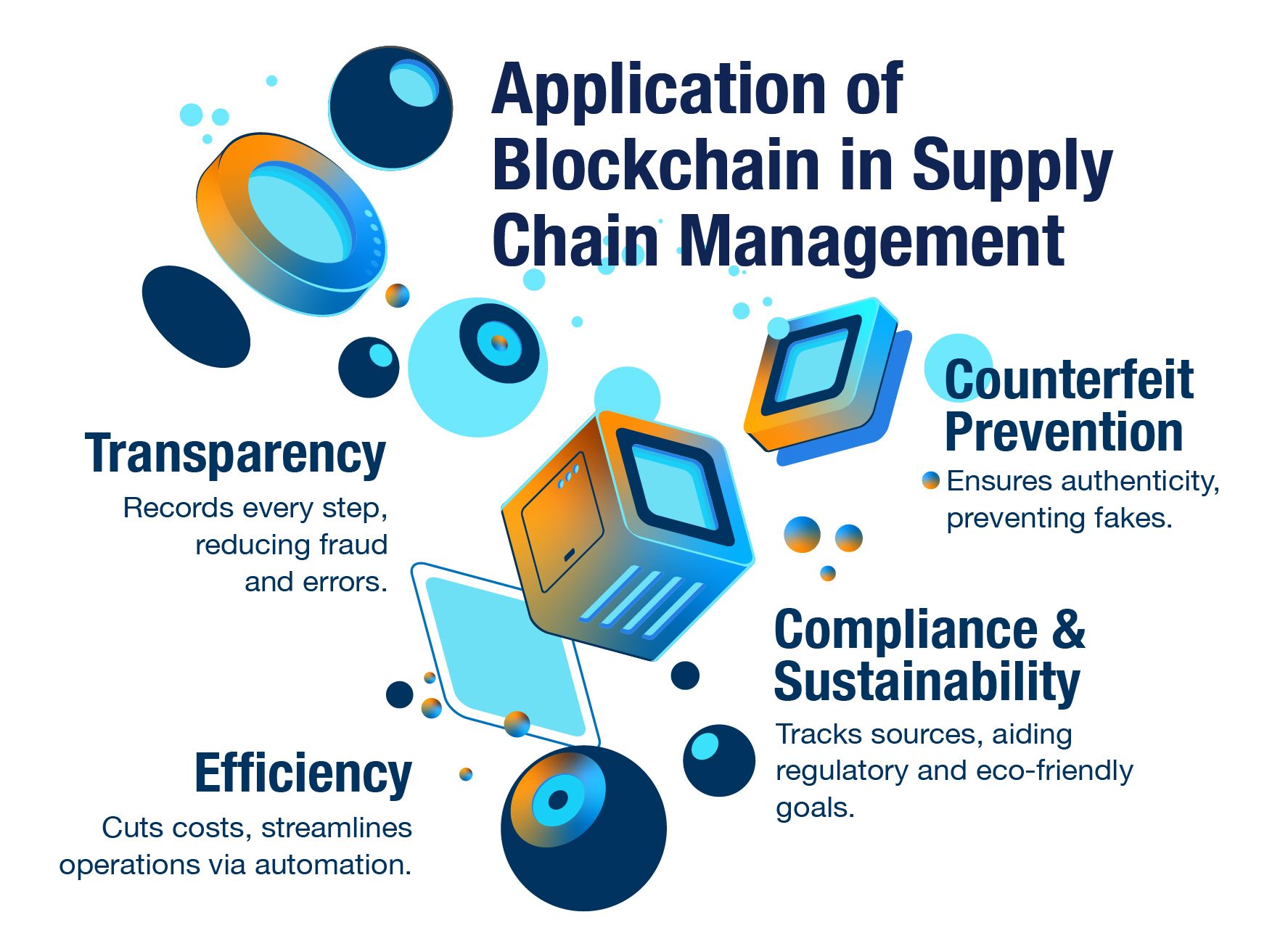
Applications of Blockchain in Supply Chain Management
Blockchain in supply chain management offers several key benefits—including ensuring transparency and traceability by recording all transactions, reducing fraud, and errors. As a result, counterfeit products are also deterred due to these immutable records. Meanwhile, efficiency is improved with smart contracts and process automation, while also cutting costs. Further, the enhanced security safeguards sensitive data. In addition, supplier relationships benefit from transparent performance records. Lastly, compliance and sustainability efforts are further simplified with more accessible product data.
Use Cases and Adoption of Blockchain in Supply Chain Management
Here are instances of companies that have adopted blockchain technology in their supply chain management to enhance transparency, traceability, and efficiency:
- Walmart is utilizing blockchain technology to enhance transparency within the food supply chain. They have digitized the entire process utilizing hyperledger fabric, making it transparent, traceable, and reliable. This technology allows employees to quickly track product origins, reducing wait time from days to seconds. The digitization also minimizes paper waste while automating processes and speeding up supply chain transparency.
- De Beers, the world’s leading diamond producer, employs blockchain technology through its platform “Tracr” to monitor the journey of every natural diamond from mine to retail. Tracr serves as a tool to verify diamond authenticity and prevent the sourcing of gems from conflict zones that may fund violence. De Beers’ CEO, Bruce Cleaver, highlights that Tracr enables comprehensive diamond tracking within the supply chain, providing unprecedented asset traceability assurance that was previously unattainable.
- Ford Motor Company implemented blockchain technology for tracking cobalt supplies essential for electric car batteries. The technology traces cobalt from its source, ensuring authenticity and quality standards. Through blockchain, Ford can record the cobalt’s origin during mining and monitor the journey throughout the supply chain, enhancing transparency and authenticity verification.
Challenges and Considerations of Blockchain in Supply Chain
Blockchain technology has the potential to transform supply chain management, but it’s important to acknowledge key challenges and considerations for successful implementation:
- Human element:
Blockchain’s distinctive feature is data immutability; however supply chains often rely on human-entered data, which is prone to errors. Unlike non-blockchain systems, fixing inaccuracies in blockchain-recorded data is more challenging, requiring updates instead of traditional corrections. Each data update triggers a transaction, resulting in increased processing requirements and resource consumption.
- Scalability:
Compared to traditional databases, blockchain solutions face slower transaction processing times as transactions require validation across multiple computers or servers. Furthermore, in supply chain applications with a high-transaction volume, implementing a permissionless blockchain can become costly due to the transaction fees needed to support miner nodes creating blocks. With some supply chains involving millions of daily transactions, scalability planning is essential during implementation.
- Upfront cost:
The initial expenses involved in adopting a blockchain solution can be substantial. These include hiring specialized blockchain developers, who typically demand higher compensation than traditional developers due to their expertise. Additionally, planning, licensing, and ongoing maintenance costs further contribute to the overall substantial investment.
Private Equity Investments in Blockchain Supply Chain
Private equity companies are channeling investments into blockchain supply chain enterprises driven by multiple factors. Firstly, they hold the conviction that blockchain technology harbors the potential for a paradigm shift in supply chain management. Secondly, they perceive a burgeoning need across businesses of varying sizes for blockchain-driven supply chain solutions. Lastly, private equity recognizes a substantial opportunity to achieve appealing returns on their investments in this domain.
Some notable activities:
- Celsius Network:
This company has developed an online financial platform with the aim of enabling secure digital asset trading. By democratizing interest income, the lending platform offers members access to exclusive financial services not typically offered by conventional financial institutions. Additionally, the company's digital wallet provides interest on deposits, offering businesses a novel avenue for earning, borrowing, and conducting transactions on the blockchain. On June 6, 2023, Fahrenheit Holdings completed a $2B leveraged buyout (LBO) to acquire the company.
- Infogain:
A provider of IT services for various industries, Apax Partners acquired the company through an $850M LBO on June 11, 2021. This investment aims to enhance Infogain’s solution portfolio, support strategic acquisitions, facilitate geographical expansion, and grow its workforce.
However, it’s important to recognize there exist certain investment risks related to blockchain supply chain companies. One being the technology’s nascent developmental stage, with uncertain widespread adoption. Additionally, the absence of regulatory frameworks in the blockchain domain may introduce uncertainties for both businesses and investors.
Conclusion
Stax has deep expertise within the supply chain space, providing invaluable insights to both investors and businesses alike. Project-related experience includes comprehensive market analyses, identifying promising investment opportunities, and delivering data-driven insights. The firm serves a diverse range of investor interests, with a particular emphasis on upstream assets, including input suppliers and manufacturers. Stax, in our 30+ years of operation, has assisted clients exploring various subsegments within the supply chain sector. With a profound understanding of the complete supply chain ecosystem, Stax stands as the leading strategy consulting firm for comprehensive market outlooks and stability trends. To learn more about Stax and our services, visit
www.stax.com
or
click here to contact us.
- AWS. “What Is Blockchain Technology?,” accessed Sep. 2023.
- Deloitte. “Using blockchain to drive supply chain transparency,” Jun. 2023.
- Rosencrance, Linda. “7 Applications of Blockchain in the Supply Chain,” Technopedia, Jul. 2023.
- Ashcroft, Sean. “Top 10 uses of blockchain in supply chain,” Supply Chain Digital, Mar. 2023.
- Hayes, Adam. “Blockchain Facts: what is it, how it works, and how it can be used,” Investopedia, Apr. 2023.
- Synopsys. “Blockchain,” accessed Oct. 2023.
- Bain & Company. “Web3 Remains Highly Relevant for Private Equity,” Feb. 2023.
- Thomas, Dylan. “Private equity's blockchain adoption may clear path to retail investors,” S&P Global Market Intelligence, Oct. 2023.
- Emergen Research. “Top 7 Leading Companies in the Blockchain Supply Chain Industry,” Apr. 2023.
- Blockchain Council. “Top Companies Using Blockchain To Increase Supply Chain Management,” Nov. 2020.
- Dilmegani, Cem. “12 Blockchain in Supply Chain Case Study in 2023c” AI Multiple, Jun. 2023.
- Turpitka, Dennis. “Five Challenges To Prepare For When Using Blockchain For Supply Chain Operations,” Forbes, Sep. 2020.
- Lawton, George. “10 blockchain problems supply chains need to look out for,” Tech Target, Apr. 2019.
- Foley & Lardner LLP. “The Pros and Cons of Blockchain in Supply Chain,” JD Supra, Aug. 2021.
- Pitchbook: Stax analysis. “PE deals in Blockchain,” JD Supra, retrieved Oct 2023.