Share
Two decades ago, digital evidence—evidence for crime stored in electronic devices, was not a major part of criminal investigations.1 However, according to a study conducted by IBM, digital evidence is at the heart of most lawsuits−appearing in more than 90% of all crimes committed today.4
Investigations for crimes ranging from homicides to abductions to domestic violence, involve significant volumes of evidence stored in electronic devices. Which has led to the need for policy changes and regulations, resulting in the establishment of the Digital Evidence Task Force (DETF) by the International Association of Chiefs of Police (IACP).2
Today,
AI and machine learning interventions help to simplify and accelerate the investigation process as it enables law enforcement to scrape through large volumes of data effortlessly.2
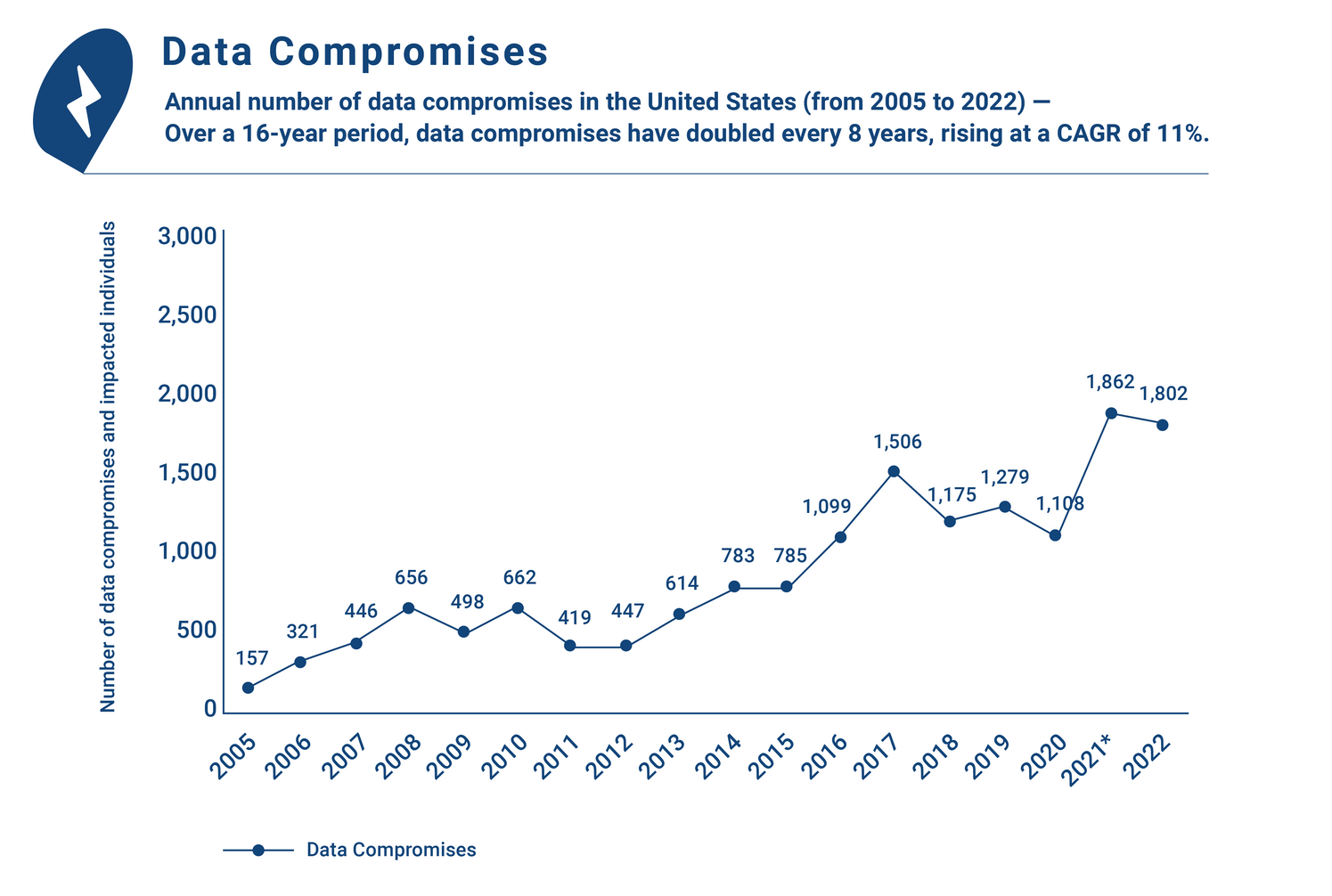
The rise of data compromises in businesses has also led to an increased demand for digital forensics. In fact, a 2022 study reveals that cyber-criminals could breach a businesses’ network in 93% of the cases.6 Over a 16-year period, data compromises have doubled every 8 years. In 2006, there were 321 data compromises. Fast forward to 2022, the number stands at a staggering 1802, rising at a CAGR of 11%.7 Additionally, a 2022 Forbes article states that 20% of companies had at least of one data compromise in 2021.17 These data compromises can be correlated to increased digital transformation strategies adopted during the pandemic. According to a cybersecurity survey by the World Economic Forum, 81% of C-Suite personnel cite digital transformation as the key driver of cybersecurity resilience.
Rising demand has also led to recent significant private equity deals in digital forensics surpassing $1 billion per transaction. Most recently, in January 2023, Thoma Bravo agreed to acquire Magnet Forensics, a Canadian player in the digital forensics space for C$1.8B.12
Organizations are increasing cyber budgets
In 2022, 83% of companies reported they had more than one data breach−resulting in firms charging higher prices from end consumers to combat these costs.8
The cost of data breaches in organizations with no deployment of AI and automation ranged between $6.05M to $6.20M (2020-2022). On the other hand, organizations that deployed AI and automation made huge cost savings. These savings accounted to half the average cost of a data breach even without a full AI deployment− subsequently leading to an increase in cyber budgets.8
The U.S. government has also proposed to increase the civilian cybersecurity budget to $10.9 billion in 2023;15 a 11% increase compared to 2022.14 Of the 2023 budget, $2.5 billion was allocated to Department of Homeland Security’s Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Agency (CISA) to protect federal infrastructure16 −further validating the growth in this segment.16
Small businesses are attractive cyber-attack targets
A recent Forbes article reveals that small businesses are three times more likely to be subject to cybersecurity threats than large companies. This is because small businesses lack the necessary resources to protect themselves. High-value accounts at C-Suite level in small organizations are two times more likely to be hacked compared to that of an average employee.5 A 2021 report states that 70% of small businesses fell victim to ransomware attacks.13 Ransomware is a type of cyberthreat that involves permanently blocking access to a device the victim owns until a ransom is paid. These types of cyberthreats led to the establishment of the Ransomware Task Force by the U.S. government officials, academics, and members of think-tanks, and the private sector.13
A 2022 article by Forrester states SMBs need to have a sound strategy to reduce the time to respond to such incidents indicating an increasing demand for digital forensics.9 Another 2022 article states that by 2025, half of the SMBs will utilize Managed Detection and Response (MDR) services, a cybersecurity service used for threat hunting.9
Web, finance, tech, education, and health, among vulnerable sectors
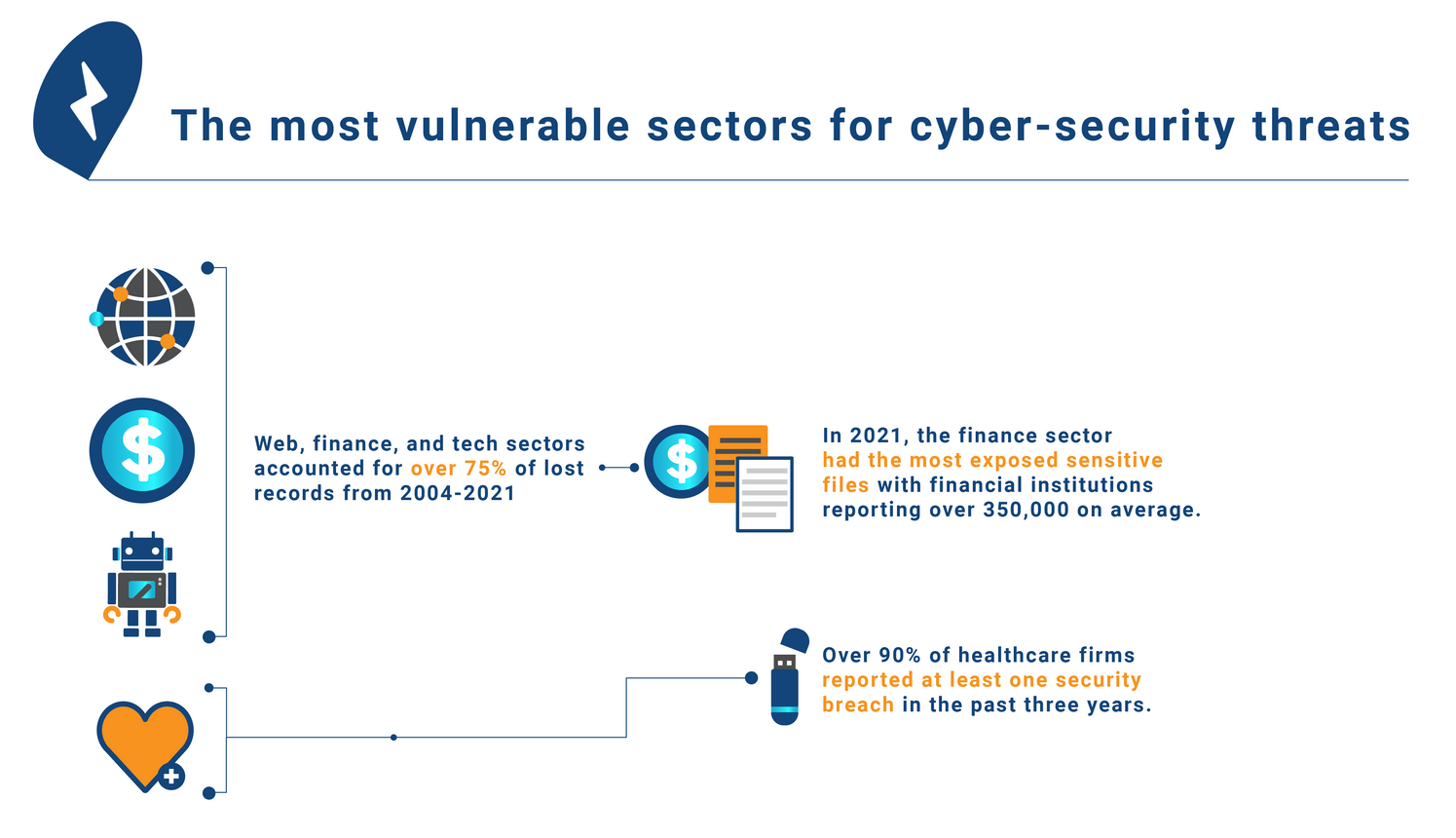
During 2004-2021, web, finance and tech were the most vulnerable sectors.6 These industries together accounted for over 75% of lost records.6 The finance sector had the highest level of exposed sensitive files in 2021 with financial institutions reporting over 350,000 exposed sensitive files on average. The increased exposure in finance was exacerbated by the increased usage of mobile banking during the pandemic.10 Healthcare, education, and government sectors also witnessed rising levels of data breaches.10 This was primarily evident post-pandemic. The cyber-attacks faced by the healthcare sector in 2020 was twice the levels in 2019. In the past three years, over 90% of all firms in the healthcare sector reported at least one security breach.10 These indicate a rising interest for digital investments in these sectors.
A focus area for investors
Rising digital evidence and data breaches signal significant growth potential of digital forensics. The purposes cover both criminal investigations by the defense forces as well as cybersecurity threat mitigation by organizations. Small businesses and sectors including finance, technology, and healthcare are the most vulnerable. As such, these sectors require sound mitigation strategies.
Investors should consider investments in digital forensics software for criminal investigations. They should also watch out for solutions that affect other vulnerable sectors. There are specific threats such as ransomware that affect small businesses and industries at-risk. Hence, it may also be worthwhile considering investments in solutions such as MDR software that address such risks.
References
- Discover how technology helps manage the growth in digital evidence, David Williams, Microsoft Industry Blogs, 2022
- Digital Evidence Task Force, IACP, 2019
- 2022 cybersecurity forecasts predict growth, emphasizing resilience, Louis Columbus, VentureBeat, 2022
- Meeting the Future of Digital Forensics and Evidence Management, IBM, 2022
- Small Businesses Are More Frequent Targets Of Cyberattacks Than Larger Companies: New Report, Edward Segal, Forbes, 2022
- Alarming Cyber Statistics For Mid-Year 2022 That You Need To Know, Chuck Brooks, Forbes, 2022
- Annual number of data compromises and individuals impacted in the United States from 2005 to 2022, Statista, 2023
- Cost of a Data Breach Report 2022, IBM, 2022
- Why managed detection and response (MDR) adoption is growing among small businesses, Louis Columbus, VentureBeat, 2022
- 6 Industries Most Vulnerable to Cyber Attacks, Western Governors University, 2021
- Data Breach Investigations Report, Verizon, 2022
- Magnet Forensics Inc. Enters into Definitive Agreement to be Acquired by Thoma Bravo, Thomas Bravo, 2023
- Ransomware attacks are hitting small businesses. These are experts' top defense tips, Jenna McLaughlin, npr, 2022
- White House Proposes $10.9 Billion Budget for Cybersecurity, Eduard Kovacs, Wired Business Media, 2022
- Budget of the U.S. Government FISCAL YEAR 2023, The White House, 2022
- Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency Budget Overview, Department of Homeland Security, 2022
- Small Businesses Are More Frequent Targets Of Cyberattacks Than Larger Companies: New Report, Edward Segal, Forbes, 2022






