Share
U.S. Oil Production Surge Faces 2024 Slowdown
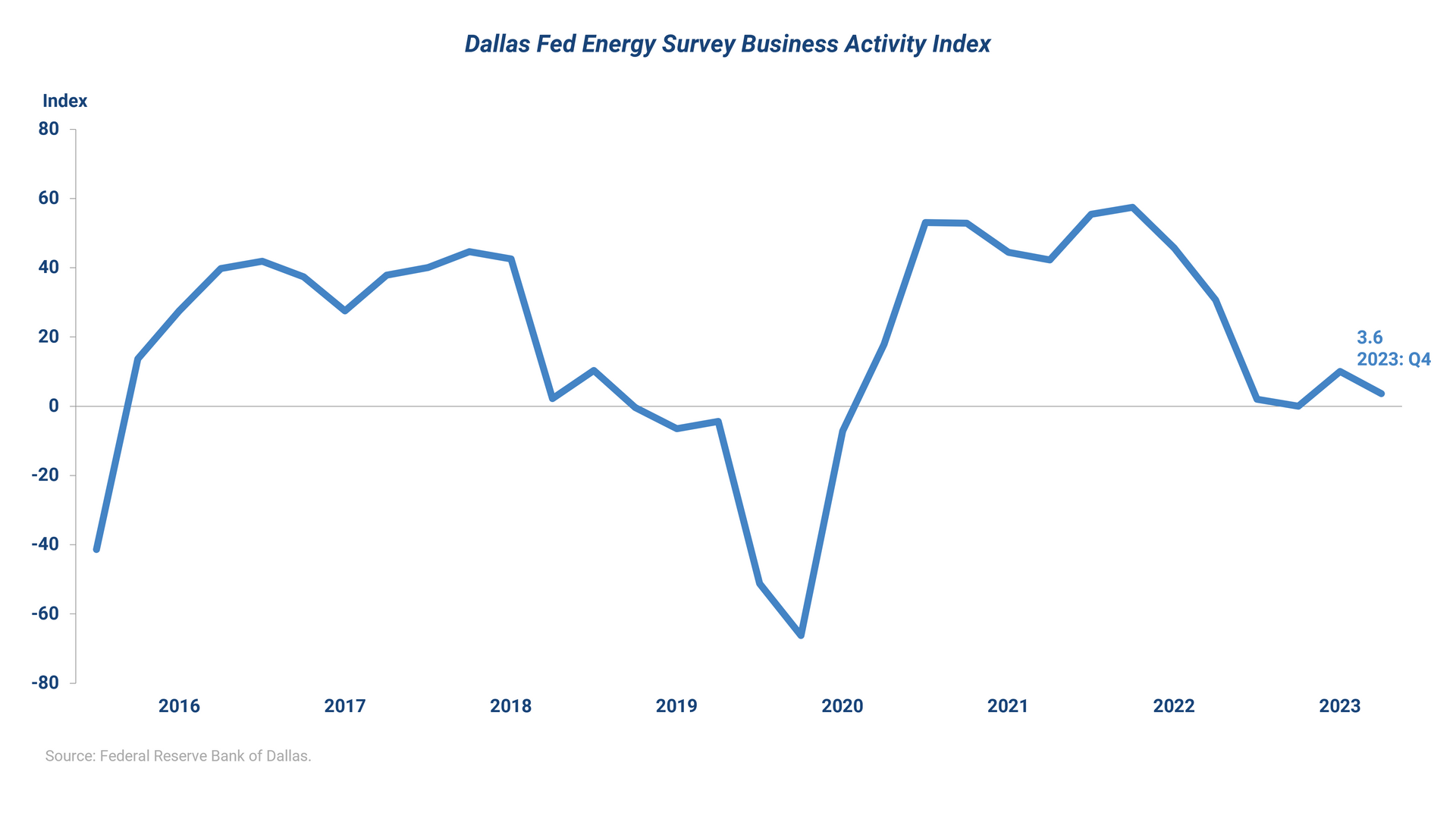
The energy market is currently perceived as being “well supplied,” which is expected to restrict the growth of production volume. The U.S., now the world’s largest oil producer, has seen its crude production average 12.9 million barrels a day in 2023, according to the U.S. EIA. This surpasses the previous record of 12.3 million barrels per day set in 2019, attributed to increased E&P output from private operators, improvements in drilling and completions, and a significant decrease in drilled but uncompleted (DUC) wells. However, these factors are unlikely to persist, leading the U.S. EIA to forecast a significant slowdown in oil production in 2024. This outlook is corroborated by a recent Dallas Fed Energy Survey, indicating waning activity within the oil and gas sector in the fourth quarter of 2023.
Conflicting demand trends are also evident in the market, which is helping to keep production volumes rangebound. A strong U.S. economy and increased demand from plastics and aviation end-markets is being offset by factors such as warmer temperatures, the expansion of electric vehicles, a shift towards cleaner technologies, and weaker economic growth in international markets (such as China). This combination of factors is expected to result in stagnant demand growth.
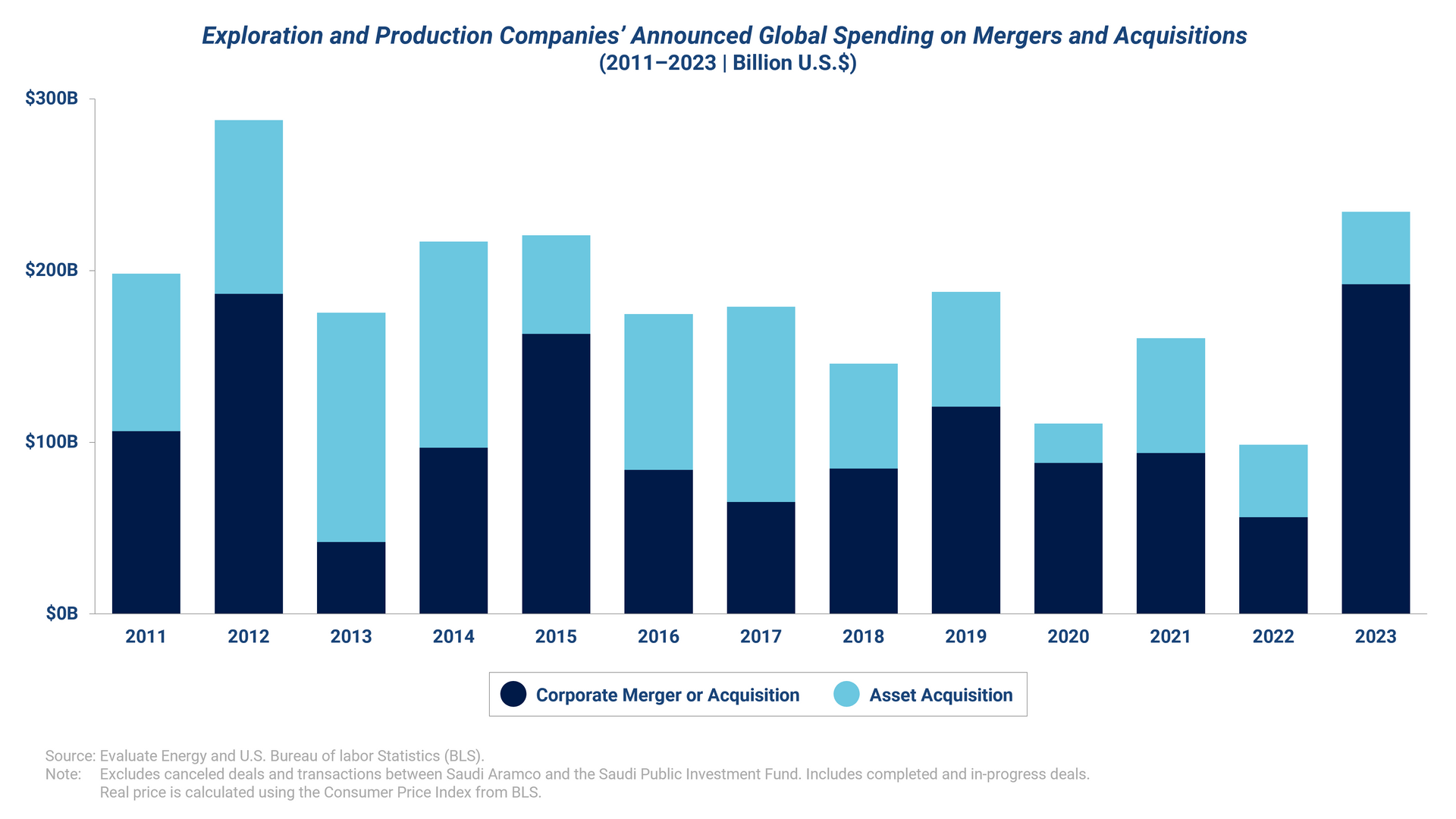
Even before the pandemic, the oil and gas industry was undergoing a significant transformation, evidenced by the shale revolution, oil price volatility, and advancements in energy efficiency. These developments presented numerous challenges for operators, who needed to strike a balance with operational efficiency, production optimization, and the reduction of capital expenditures. Oil and gas operators, particularly public companies, focused on optimization and capital efficiency, a trend that has persisted into 2023-2024. Rather than investing heavily in capital expenditures to boost exploration and drilling activity, public oil and gas firms are now concentrating their efforts on maximizing financial value and return on investment. M&A has been valuable lever, enabling O&G operators to grow by expanding acreage through acquisition.
Driving Factors for M&A Surge and Energy Transition in O&G
Capital discipline has enabled O&G companies to build and maintain strong cash balance sheets, affording them the financial flexibility to pursue acquisitions. These M&A transactions have enabled oil and gas operators to boost production and profitability through the acquisition of proven reserves, instead of allocating capital expenditure towards exploration and development. Furthermore, the purchase of companies or assets in geographies that complement acquirers’ existing portfolios enables operators to increase efficiency and lower operating costs.
In particular, oil and gas companies with operations in the Permian basin, boasting productive shale oil output, substantial undeveloped reserves, and essential upstream infrastructure, have been attractive targets for producers seeking to increase their inventory. More specifically, Permian deals accounted for more than 40% of deals (by value) in 2023 and half of M&A transactions since 2014.
In addition, current macroeconomic factors are likely to spur M&A activity within smaller upstream companies, making them potential targets for acquisition. As production volumes moderate, these smaller players are facing challenges in maintaining profitability. They lack the economies of scale and operational efficiency of larger players, making it difficult to reduce operating costs amidst slowing production volume growth. Furthermore, these smaller upstream operators continue to encounter tighter credit conditions and higher costs of capital—all of which may lead to more M&A in the near future.
M&A activity could also drive operators to shift their focus from fossil fuels to alternative energy sources like renewables. Despite pledges for “net zero” emissions, oil and gas companies have slowed their pivot to renewables. The Ukraine conflict, for example, has exposed the importance of countries mitigating energy supply risks. Additionally, rising costs of rare earth metals and related input costs as well as higher interest borrowing costs have adversely affected renewable investments, causing operators to curtail their decarbonization initiatives.
However, as these challenges may now be perceived to be less risky, achieving net-zero emissions may regain prominence, especially for European and public companies. M&A activities can help accelerate operators’ diversification away from fossil fuels and reshape their portfolios through investment in renewable natural gas (RNG), hydrogen, carbon capture, and related assets.
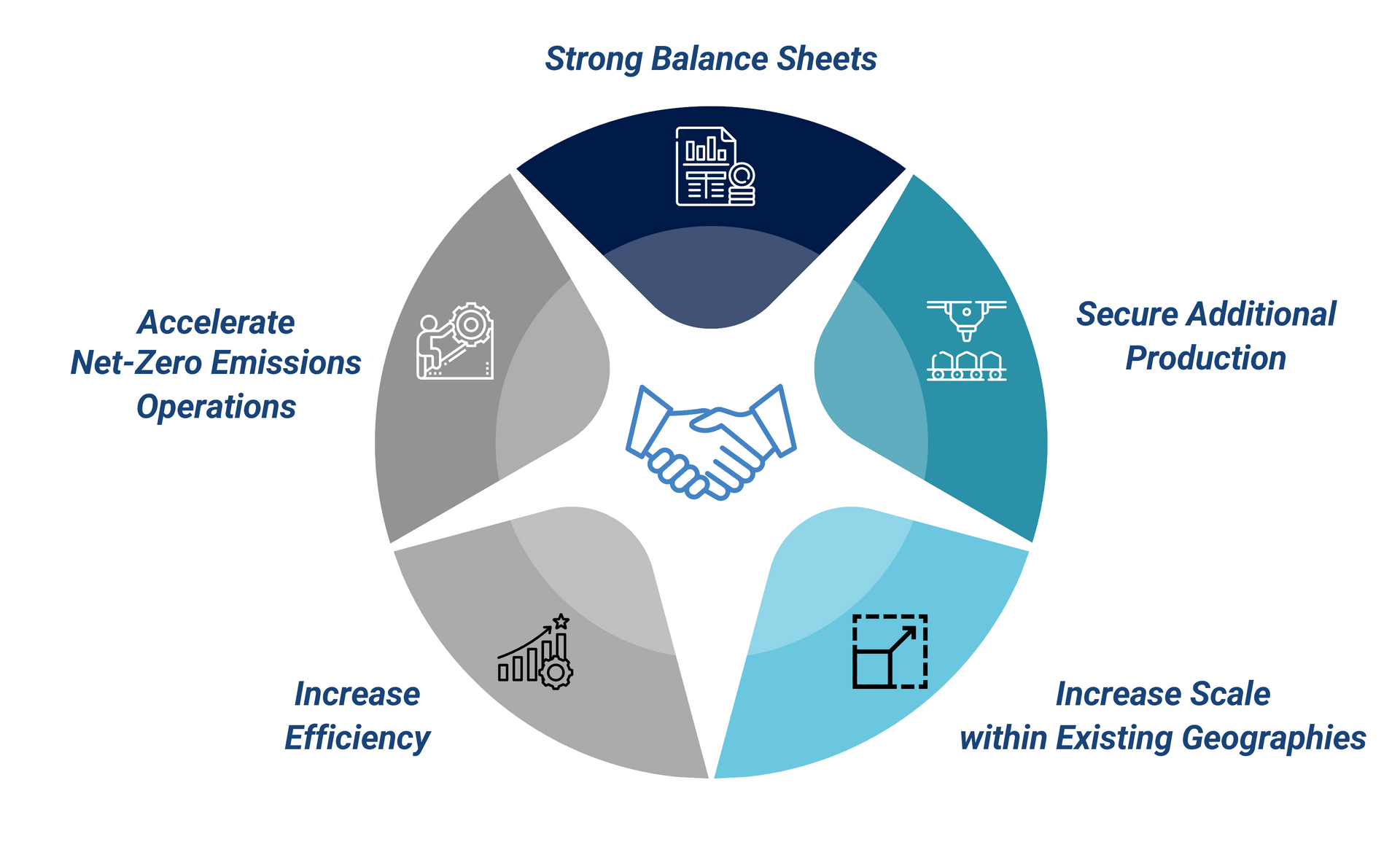
The M&A landscape in the oil and gas industry during 2023 underscored the sector's resilience and strategic shifts amidst global economic and environmental challenges. Looking ahead to 2024, the industry is poised for continued consolidation, driven by a complex interplay of market dynamics, strategic imperatives, and the overarching trend towards energy diversification. The sector's ability to adapt and evolve through strategic M&A will be crucial in navigating the forthcoming challenges and seizing opportunities.
About Stax
When it comes to understanding the viability of a market for investment, Stax is where value is created. Our approach, centered around providing data-driven and actionable insights, enables clients to make informed decisions that lead to providing the most competitive returns. To learn more about Stax and our services, visit www.stax.com or click here to contact us.







